假如給物種貼上條形碼
假如給物種貼上條形碼
當我們踏入一家超市,麵對琳琅滿目的商品的,我們不禁要感歎現代社會商品種類的豐富程度已經如此之高,生產運輸以及管理的高效也讓人讚歎不已。在這種驚歎和好奇之於,我們不由得發問,是什麽讓這一切運轉的如此高效和順利呢?其實最關鍵的是信息化的引入,是電腦和數據庫的使用整個過程和流暢,其中最典型的例子就是條形碼的應用。當我們付款的時候,收銀員隻需將條碼對著識別器掃一下就會出現商品的價格,這是因為條碼的本質上一套“語言”係統,隻不過不是人可以閱讀的,而是計算機識別的,這些間隔和粗細不同的條帶構成了基本語句,裏麵包含了商品的生產信息,運輸信息,價格信息等等。
所以條形碼的核心就是用一套編碼的規則將獨一無二的信息編碼成一個唯一的識別碼。聽起來是很樸素的一個道理,往往也是簡單的規則就有更大的使用場景。這不,生物學家就在想,自然界這麽多物種類別如何按照相同的思路構建出一套鑒定係統呢?傳統的分類工作是通過分類學家根據自己的經驗,通過肉眼觀察將物種分門別類,劃分到不同的分類單元(界門綱目科屬種)。例如我們人就屬於哺乳綱靈長目人科人屬人種,和我們形態相近的猿類也屬於靈長類。如果是大型的動物還好觀察,但如果是非常小的昆蟲,就不得不借助放大鏡或者顯微鏡觀察了,有時候甚至沒有成蟲,隻有非常小的卵,這種情況下是很難鑒定出來是什麽物種的。而很多昆蟲都是全變態昆蟲,他們的幼蟲和成蟲的形態相去甚遠,真是讓人傻傻分不清 (圖1)。但往往現實中這種工作是必須的,比如在海關檢驗檢疫過程中,水果和蔬菜裏麵殘存的卵或者部分組織是需要快速準確的被鑒定出來的。以防物種入侵的危害。所以這種通過傳統觀察的方式似乎在某些情況下就顯得無能為力了,換句話說這種由生物學特征組成的信息不適合作為快速分類的基礎。另外這種通過觀察的工作十分依賴分類學家,在我們的印象中往往是頭發花白上了年紀的老頭,現在學習和研究分類學的人越來越少。那我們可以用什麽呢?答案是分子,準確來講就是DNA序列,因為DNA遺傳物種是目前發現所有的生物(真核和原核,除一些病毒的遺傳物質可能是RNA)都具有的相同屬性。DNA測序技術的發展使得我們研究生物的手段發生了根本性的轉變。通過測序技術我們可以讀到每個物種特有的一套基因組信息。我們是不是可以考慮從這些基因組上尋找一個基因,或者一段序列來代表這個物種呢?
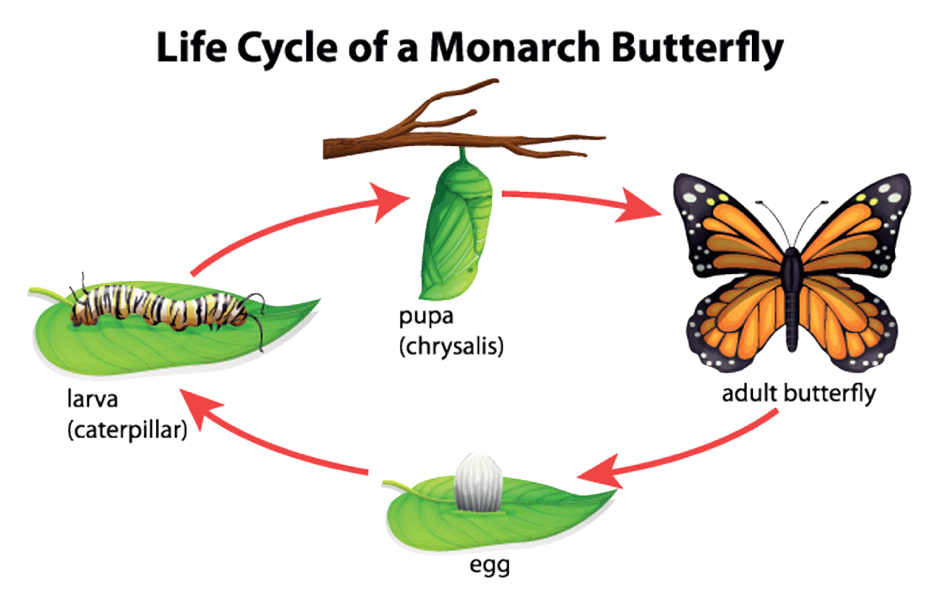
圖1, 帝王蝶的生活史
2003年加拿大圭爾夫大學的Paul Hebert等人提出了DNA條形碼的概念,他們通過對動物界中11門13320個物種分析後,正式提出將一段長648bp的線粒體細胞色素C氧化酶亞基I(cytochromecoxidaseI,COI)基因作為動物鑒定的通用條形碼序列。由於傳統分類學不能滿足現代物種鑒定的需求,DNA條形碼技術利用較短的基因保守序列進行種的鑒定,可以在更大範圍應用於生態保護研究。DNA條形碼自提出以來,受到了世界各國分類和鑒定學家的高度重視,Nature發表了題為“DNA barcoding, a useful tool for taxonomists”的文章,文中指出DNA條形碼是國際上近年來發展起來的物種鑒定新技術。Miller在PNAS上發表的文章中提出DNA條形碼技術正在推動分類學的“文藝複興”。DNA條形碼技術擺脫了傳統形態鑒定方法依賴長期經驗的障礙,通過建立標準數據庫,可實現快速準確的鑒定,是分子鑒定方法學上的創新。
如圖2所示,是DNA條形碼用來做物種鑒定的標準流程。第一步是從組織提取DNA;第二步通過PCR擴增出我們的目的片段;第三步是對PCR產物進行測序;第四步是將測序得到的結果和數據庫比對已得到相匹配的物種記錄。舉個例子,如果你去野外露營時,被不知名的蟲子咬了一口,擔心是否有毒?你可以將這個蟲子用酒精保存帶回來進行DNA條形碼測序。就可以準確知道物種的信息。DNA條形碼技術應用於生物資源具有重大意義,可以有效監控珍稀瀕危物種進、出口貿易,有利於發現新種和保護生物多樣性,可實現有害生物及入侵種的快速查驗等。目前DNA條形碼技術在生物資源中的重要實踐,比如應用於生物物種鑒定與分類,成為傳統分類方法的有力補充,在珍稀瀕危和貴重生物資源、海關貿易以及生物多樣性保護的應用方麵提供新思路。
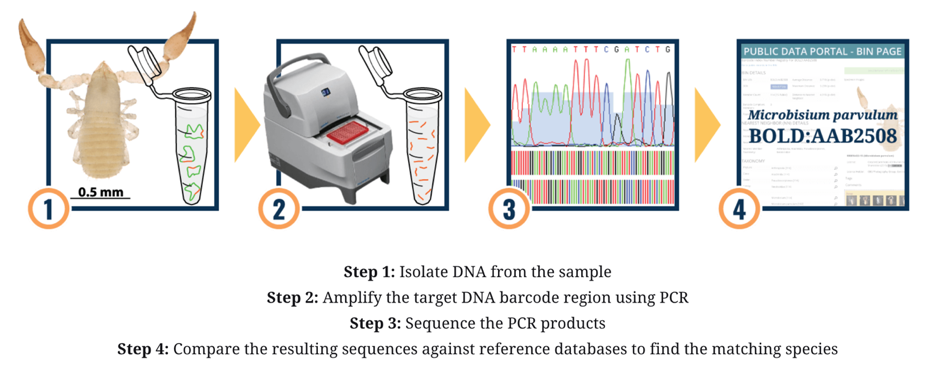
圖2,DNA條形碼用來做物種鑒定的標準流程,圖片來源()
目前通過科學家的研究已經在幾個基本的類群中找到了合適的marker基因用來做DNA條形碼,比如COI作為動物的通用條形碼序列,葉綠體上的rbcL和matK構成的複合序列作為植物的鑒定條形碼;在細菌中使用核糖體中編碼16SRNA的基因作為條形碼,而在真菌鑒定中使用ITS序列(圖3)。然而在真實的況中,這些marker基因並不是完美的解決所有問題,也會出現失效的時候,比如在一些屬的物種中,物種之間的差別非常小,反倒同一個物種的不同個體間差異很大,這樣就會造成鑒定的錯誤。因此這時候就需要尋找其他的條形碼序列代替或者補充。在篩選DNA條形碼的時候,需要考慮其滿足這樣幾個條件:1)必須要在大部分物種中都存在這個基因或者片段;2)這個片段的長度不能太長也不能太短,太長會影響PCR過程,太短可能包含的信息就會太少,能夠編碼的信息就會越少;3)因為是需要PCR擴增,所以在這個片段的兩端需要有比較保守的序列特點,從而可以設計出通用的引物。

圖3, 不同類群的DNA條形碼序列
目前,由國際生命條形碼聯盟建立的第一個國際DNA條形碼數據庫BOLD已收錄了30.6萬個物種的776.3萬條DNA條形碼序列(截止到2019年12月)。研究者可以登錄係統通過物種名稱來搜索相關物種的DNA條形碼數據,或者提交序列來鑒定該物種的分類信息 (圖4)。隨著研究的不斷深入,DNA條形碼數據庫將得到不斷地補充和擴展,結合計算機信息係統,可實現物種鑒定的標準化和自動化,將在生物分類學方麵發揮巨大作用。


圖4,人的COI序列和條形碼效果圖,圖片來源()
參考文獻:
Hebert, Paul DN, et al. "Biological identifications through DNA barcodes." Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences 270.1512 (2003): 313-321.
Schindel, David E., and Scott E. Miller. "DNA barcoding a useful tool for taxonomists." Nature 435.7038 (2005): 17-18.
Miller, Scott E. "DNA barcoding and the renaissance of taxonomy." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 104.12 (2007): 4775-4776.
陳士林 [1, et al. 生物資源的 DNA 條形碼技術. Diss. 2013.
當我們踏入一家超市,麵對琳琅滿目的商品的,我們不禁要感歎現代社會商品種類的豐富程度已經如此之高,生產運輸以及管理的高效也讓人讚歎不已。在這種驚歎和好奇之於,我們不由得發問,是什麽讓這一切運轉的如此高效和順利呢?其實最關鍵的是信息化的引入,是電腦和數據庫的使用整個過程和流暢,其中最典型的例子就是條形碼的應用。當我們付款的時候,收銀員隻需將條碼對著識別器掃一下就會出現商品的價格,這是因為條碼的本質上一套“語言”係統,隻不過不是人可以閱讀的,而是計算機識別的,這些間隔和粗細不同的條帶構成了基本語句,裏麵包含了商品的生產信息,運輸信息,價格信息等等。
所以條形碼的核心就是用一套編碼的規則將獨一無二的信息編碼成一個唯一的識別碼。聽起來是很樸素的一個道理,往往也是簡單的規則就有更大的使用場景。這不,生物學家就在想,自然界這麽多物種類別如何按照相同的思路構建出一套鑒定係統呢?傳統的分類工作是通過分類學家根據自己的經驗,通過肉眼觀察將物種分門別類,劃分到不同的分類單元(界門綱目科屬種)。例如我們人就屬於哺乳綱靈長目人科人屬人種,和我們形態相近的猿類也屬於靈長類。如果是大型的動物還好觀察,但如果是非常小的昆蟲,就不得不借助放大鏡或者顯微鏡觀察了,有時候甚至沒有成蟲,隻有非常小的卵,這種情況下是很難鑒定出來是什麽物種的。而很多昆蟲都是全變態昆蟲,他們的幼蟲和成蟲的形態相去甚遠,真是讓人傻傻分不清 (圖1)。但往往現實中這種工作是必須的,比如在海關檢驗檢疫過程中,水果和蔬菜裏麵殘存的卵或者部分組織是需要快速準確的被鑒定出來的。以防物種入侵的危害。所以這種通過傳統觀察的方式似乎在某些情況下就顯得無能為力了,換句話說這種由生物學特征組成的信息不適合作為快速分類的基礎。另外這種通過觀察的工作十分依賴分類學家,在我們的印象中往往是頭發花白上了年紀的老頭,現在學習和研究分類學的人越來越少。那我們可以用什麽呢?答案是分子,準確來講就是DNA序列,因為DNA遺傳物種是目前發現所有的生物(真核和原核,除一些病毒的遺傳物質可能是RNA)都具有的相同屬性。DNA測序技術的發展使得我們研究生物的手段發生了根本性的轉變。通過測序技術我們可以讀到每個物種特有的一套基因組信息。我們是不是可以考慮從這些基因組上尋找一個基因,或者一段序列來代表這個物種呢?

圖1, 帝王蝶的生活史
2003年加拿大圭爾夫大學的Paul Hebert等人提出了DNA條形碼的概念,他們通過對動物界中11門13320個物種分析後,正式提出將一段長648bp的線粒體細胞色素C氧化酶亞基I(cytochromecoxidaseI,COI)基因作為動物鑒定的通用條形碼序列。由於傳統分類學不能滿足現代物種鑒定的需求,DNA條形碼技術利用較短的基因保守序列進行種的鑒定,可以在更大範圍應用於生態保護研究。DNA條形碼自提出以來,受到了世界各國分類和鑒定學家的高度重視,Nature發表了題為“DNA barcoding, a useful tool for taxonomists”的文章,文中指出DNA條形碼是國際上近年來發展起來的物種鑒定新技術。Miller在PNAS上發表的文章中提出DNA條形碼技術正在推動分類學的“文藝複興”。DNA條形碼技術擺脫了傳統形態鑒定方法依賴長期經驗的障礙,通過建立標準數據庫,可實現快速準確的鑒定,是分子鑒定方法學上的創新。
如圖2所示,是DNA條形碼用來做物種鑒定的標準流程。第一步是從組織提取DNA;第二步通過PCR擴增出我們的目的片段;第三步是對PCR產物進行測序;第四步是將測序得到的結果和數據庫比對已得到相匹配的物種記錄。舉個例子,如果你去野外露營時,被不知名的蟲子咬了一口,擔心是否有毒?你可以將這個蟲子用酒精保存帶回來進行DNA條形碼測序。就可以準確知道物種的信息。DNA條形碼技術應用於生物資源具有重大意義,可以有效監控珍稀瀕危物種進、出口貿易,有利於發現新種和保護生物多樣性,可實現有害生物及入侵種的快速查驗等。目前DNA條形碼技術在生物資源中的重要實踐,比如應用於生物物種鑒定與分類,成為傳統分類方法的有力補充,在珍稀瀕危和貴重生物資源、海關貿易以及生物多樣性保護的應用方麵提供新思路。

圖2,DNA條形碼用來做物種鑒定的標準流程,圖片來源()
目前通過科學家的研究已經在幾個基本的類群中找到了合適的marker基因用來做DNA條形碼,比如COI作為動物的通用條形碼序列,葉綠體上的rbcL和matK構成的複合序列作為植物的鑒定條形碼;在細菌中使用核糖體中編碼16SRNA的基因作為條形碼,而在真菌鑒定中使用ITS序列(圖3)。然而在真實的況中,這些marker基因並不是完美的解決所有問題,也會出現失效的時候,比如在一些屬的物種中,物種之間的差別非常小,反倒同一個物種的不同個體間差異很大,這樣就會造成鑒定的錯誤。因此這時候就需要尋找其他的條形碼序列代替或者補充。在篩選DNA條形碼的時候,需要考慮其滿足這樣幾個條件:1)必須要在大部分物種中都存在這個基因或者片段;2)這個片段的長度不能太長也不能太短,太長會影響PCR過程,太短可能包含的信息就會太少,能夠編碼的信息就會越少;3)因為是需要PCR擴增,所以在這個片段的兩端需要有比較保守的序列特點,從而可以設計出通用的引物。

圖3, 不同類群的DNA條形碼序列
目前,由國際生命條形碼聯盟建立的第一個國際DNA條形碼數據庫BOLD已收錄了30.6萬個物種的776.3萬條DNA條形碼序列(截止到2019年12月)。研究者可以登錄係統通過物種名稱來搜索相關物種的DNA條形碼數據,或者提交序列來鑒定該物種的分類信息 (圖4)。隨著研究的不斷深入,DNA條形碼數據庫將得到不斷地補充和擴展,結合計算機信息係統,可實現物種鑒定的標準化和自動化,將在生物分類學方麵發揮巨大作用。


圖4,人的COI序列和條形碼效果圖,圖片來源()
參考文獻:
Hebert, Paul DN, et al. "Biological identifications through DNA barcodes." Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences 270.1512 (2003): 313-321.
Schindel, David E., and Scott E. Miller. "DNA barcoding a useful tool for taxonomists." Nature 435.7038 (2005): 17-18.
Miller, Scott E. "DNA barcoding and the renaissance of taxonomy." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 104.12 (2007): 4775-4776.
陳士林 [1, et al. 生物資源的 DNA 條形碼技術. Diss. 2013.

做科普,我們是認真的!
掃描關注深i科普公眾號
加入科普活動群

- 參加最新科普活動
- 認識科普小朋友
- 成為科學小記者
上一篇:科普師網文:彈塗魚
下一篇:請收下!你有一份來自大自然的禮物
 會員登錄
會員登錄












 深圳市龍華區玉翠社區高坳新村小廣場
深圳市龍華區玉翠社區高坳新村小廣場












